Risk management at Fingrid
Fingrid’s internal control and risk management principles, which are approved by Fingrid’s Board of Directors, were updated during the year to respond to the evolving demands of the operating environment. Risk management as a whole was re-assessed on that basis. The assessment of key risks has been revised, the process has been made more efficient and the measures have been specified.

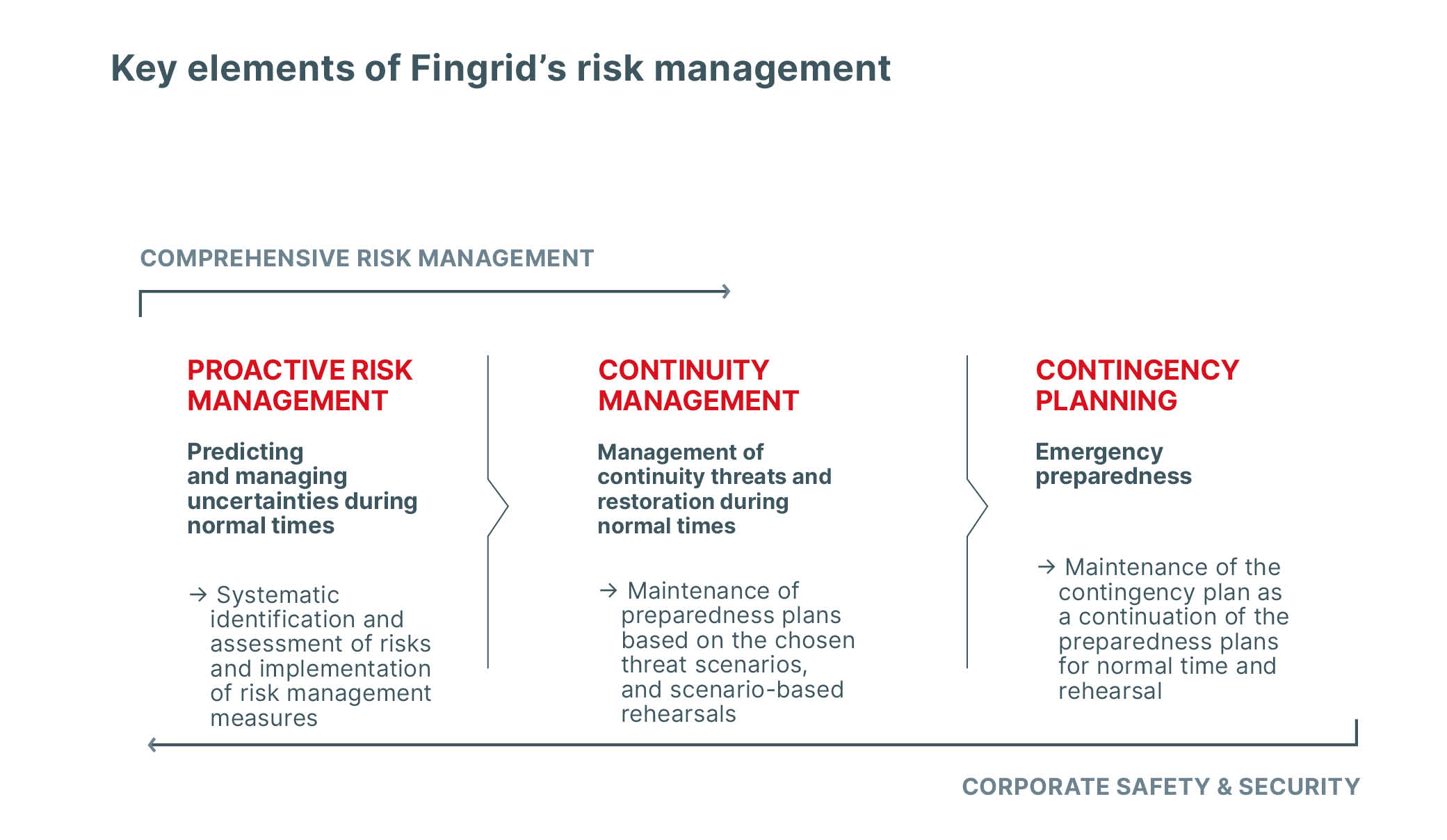
Fingrid is responsible for the functioning of Finland’s electricity system and is essentially a risk management company. Risk management is planned and governed comprehensively. The objective is to extensively identify, assess and monitor, as well as safeguard against, various threats and risks that are directed at the company’s operations, personnel and property as well as risks which also have impacts on the environment and society. Ensuring systematic corporate safety & security is a part of risk management.
Continuity management is included in comprehensive risk management, and its objective is to improve the organisation’s readiness and to prepare, in the best possible way, for the realisation of various risks and ensure the continuity of operations in such situations.
The planning of comprehensive risk management during normal times contributes to the contingency planning during societal state of emergency as required of a company with duties critical to the national security of supply.
The company’s risks are divided based on significance into strategic and major business risks to be reported to the company’s Board of Directors, and operational risks.
Risks are identified and assessed in a consistent manner as part of the company’s strategy process and in connection with significant changes affecting business operations. Risk management measures are planned, entered and followed up on regularly in the risk management system. This system was modernised during the year under review.
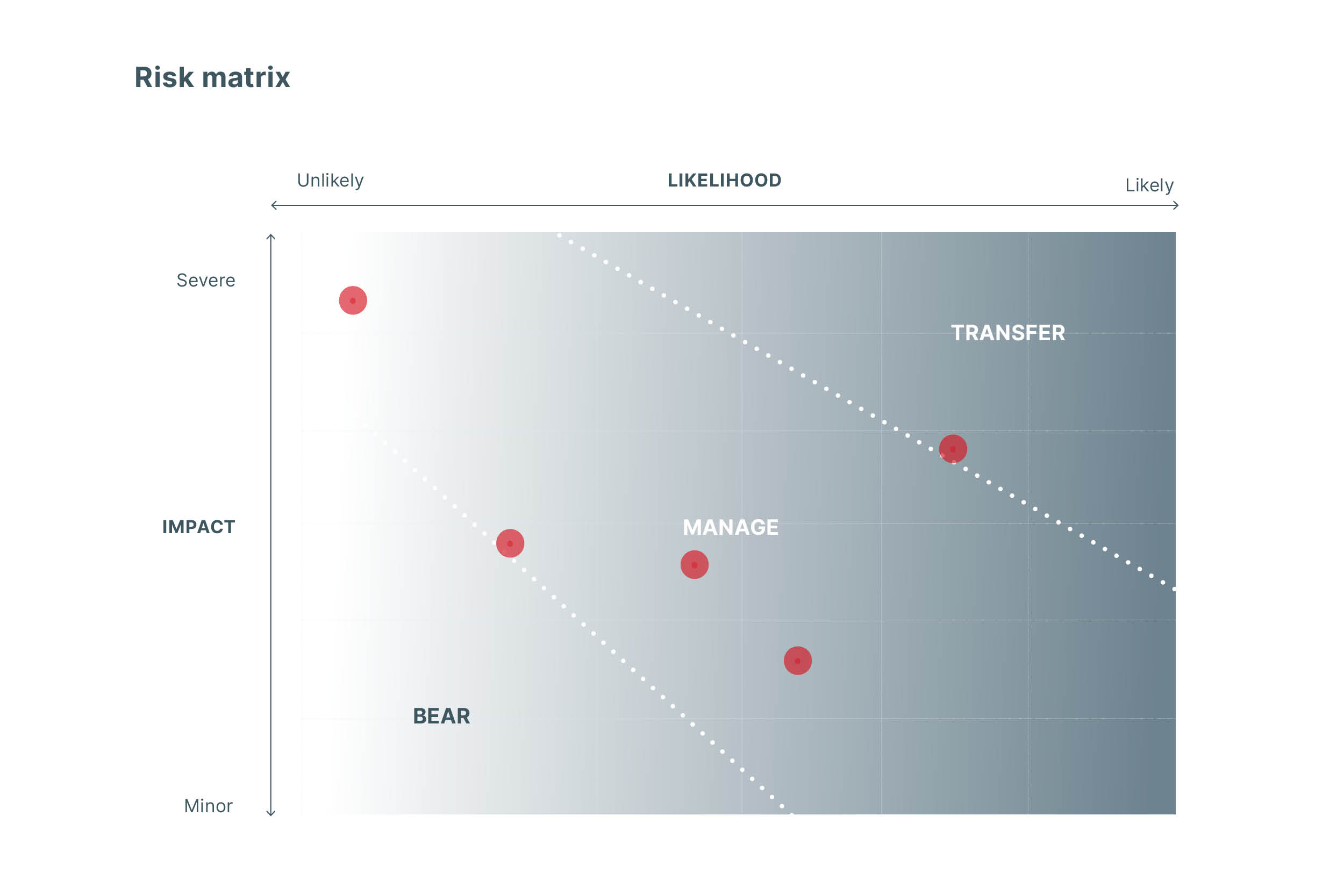
Risks identified in the risk assessment are classified in relation to the risk management measures into one of three groups:
- risk factors that are deemed significant in terms of their impacts and which are to be transferred, if possible, by contracts, insurance, derivatives or similar means,
- risk factors that are deemed moderate in terms of their impacts and which are under the company’s control through clear controls and other practical measures, and
- risk factors deemed minor in terms of their impacts but which require monitoring.
The company’s risk management is continuous, and the objective is to engage the entire personnel to identify the risks associated with the company’s operations and implement risk management measures as part of their day-to-day work. An overall risk assessment is carried out annually based on an assessment of the operating environment. The planning of risk management measures is part of strategy implementation planning. In order to manage the risks with significant impacts, risk management projects are launched as needed on the company level in order to arrange supplementary measures and monitoring.
Both strategic and financially significant business risks are reported to the company’s Board of Directors annually. Risk reporting is supplemented in connection with significant business projects and changes in the operating environment.
As a general rule, risks are protected against if the costs that the protection entails are justified in relation to the magnitude of the risk. Risks related to major personal injury and environmental damage are always protected against.
Risk protection takes place by reducing the likelihood of an adverse event and/or its impacts on Fingrid and society. The most important protection measures are:
- supporting Fingrid’s risk management culture and improving employees’ risk awareness,
- comprehensive strategy work and operational planning,
- influencing the regulation of operations,
- limiting risk through contractual arrangements,
- developing technical solutions and operations and changing procedures,
- auditing operations and reporting on and monitoring the implementation of measures and
- derivatives and insurance policies.
Continuity management, included in overall risk management, is used to reduce the direct impacts of a realised risk and to accelerate recovery from an adverse event. The planning of continuity management is based on threat scenarios that are created based on a risk and operating environment analysis. The scenarios are used to assess the company’s ability to maintain the functionality of critical processes and systems during emergencies when proactive risk management has failed. Among the scenarios that must be analysed are the loss of business premises or IT systems, a prolonged major disturbance or extreme weather conditions.
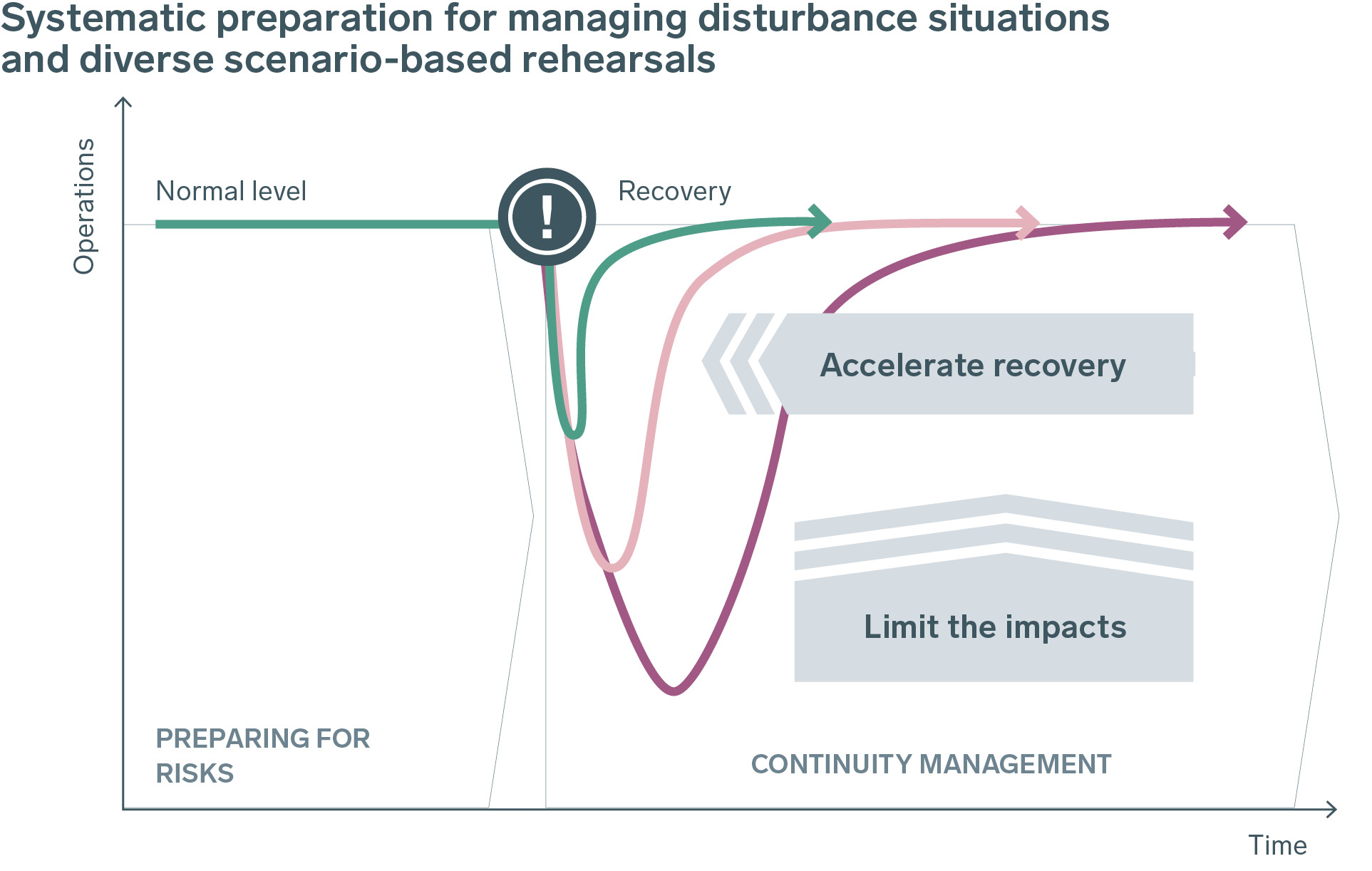
The technical and administrative preparedness required by proactive risk management and, in particular, continuity management are guided on the company level by the preparedness policy, and by the preparedness plan that the company maintains in accordance with the Finnish Electricity Market Act.
The threat scenarios are decided on as part of the company’s strategy; the necessary recovery plans are drawn up for the most significant continuity threats and their implementation is rehearsed. The rehearsals are planned together with the company’s preparedness unit.
Fingrid is a company with duties critical to the national security of supply and must be able to continue its operations even during emergencies while the Finnish Emergency Powers Act is in effect. Fingrid maintains a contingency plan as part of the preparedness plan as referred to in the Finnish Electricity Market Act. Fingrid is an active participant in the collaboration to develop the energy sector’s preparedness operations and, together with the National Emergency Supply Agency, governs the authorities’ and Finnish industries’ Electricity Pool, which co-ordinates emergency preparedness. In recent years, the Pool has invested in major preparedness rehearsals for municipal, emergency rescue and law enforcement authorities, and for the Finnish defence forces and energy companies.
At Fingrid, corporate safety & security and the related preparedness and co-operation with authorities are planned and managed as part of the company’s overall risk management. Essential elements of corporate safety & security planning and operations guidance are electrical safety and occupational safety, the safety of properties and premises, information security, personal and travel safety, emergency rescue operations and internal and external protection against crime related to the company’s business.
Risk management controls that are significant in terms of the company’s operations and finances are described and implemented by process and function to support good governance, overall efficiency, the quality of internal control and operational audits.
The preparation and description of decision-making controls take into account segregation of duties, as well as existing approval authorisations and other factors that ensure appropriate decision-making. The effectiveness of the existing controls is assessed regularly.
The company complies with the Board-approved insider guidelines and related party principles, as well as separately maintained guidelines concerning conflicts of interest and judicial disqualification.
Updated 29.4.2024

